
NCS (nerve conduction study): This is a test to see if your. The results of the EMG test can reveal nerve dysfunction, muscle dysfunction or problems with the communication between the muscles and nerves. EMG (electromyography): This test is used to find the cause of muscle weakness. This is where a needle electrode is inserted into different muscles, transmitting the electrical activity of that muscle. The second part of the study is called a needle EMG.

The first part involves nerve conduction studies using electrodes attached to the skin that help record electrical signals. How it WorksĪ physician will use electrodes to send and receive electrical impulses between the muscles and nerves. By measuring the response of the electrical impulses, the physician is able to determine if the muscles and nerves are working properly. From there, the EMG test helps the physician decide on the most appropriate treatment plan. Is a nerve conduction test painful This may feel uncomfortable, but it usually isn't painful. It depends on how many nerves and muscles your doctor tests. The EMG test can diagnosis or help rule out several conditions, including muscle disorders, peripheral nerve entrapments, nerve root entrapments or peripheral neuropathies. Nerve conduction tests may take from 15 minutes to 1 hour or more.
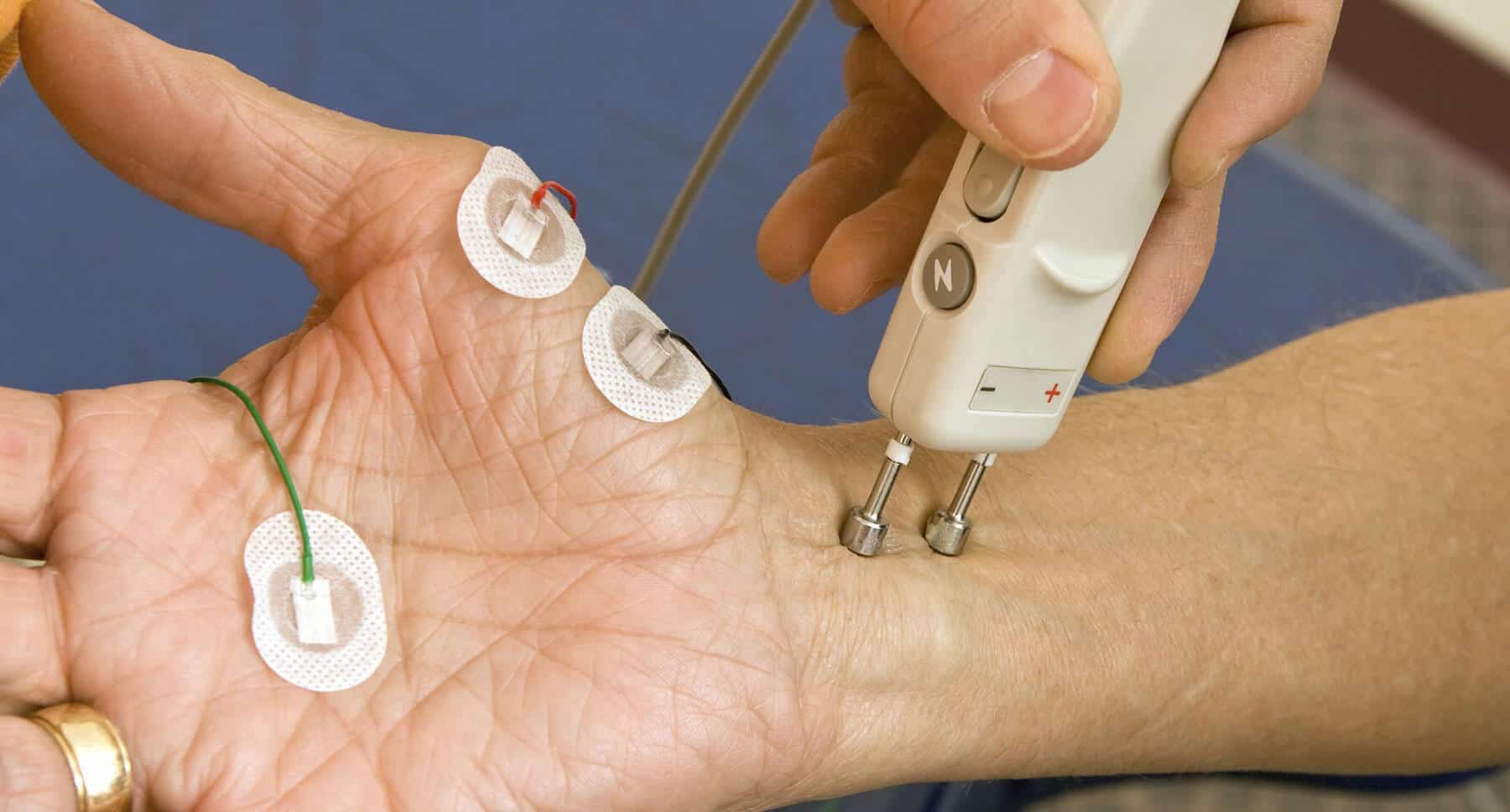
You will be asked to relax and then perform slight or full-strength muscle contractions. The most common symptoms that call for an EMG test include: If the test is painful you must tell your examiner because this can interfere with the results. Electromyography (EMG) is a diagnostic procedure used to evaluate the health and functio nality of muscles and the nerve cells that control them.Īn EMG is used to diagnosis patients who have symptoms or exam findings that could indicate a nerve or muscle disorder.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
